play withe file structure(搬运)
多图预警
content
- introduction
- file stream
- overwrite the file struction
- Exploiation of FILE struction
- FSOP
- Vtable verfication in FILE struction
- Make file struction great again
- conclusion
introduction
what happen when we use a raw io function
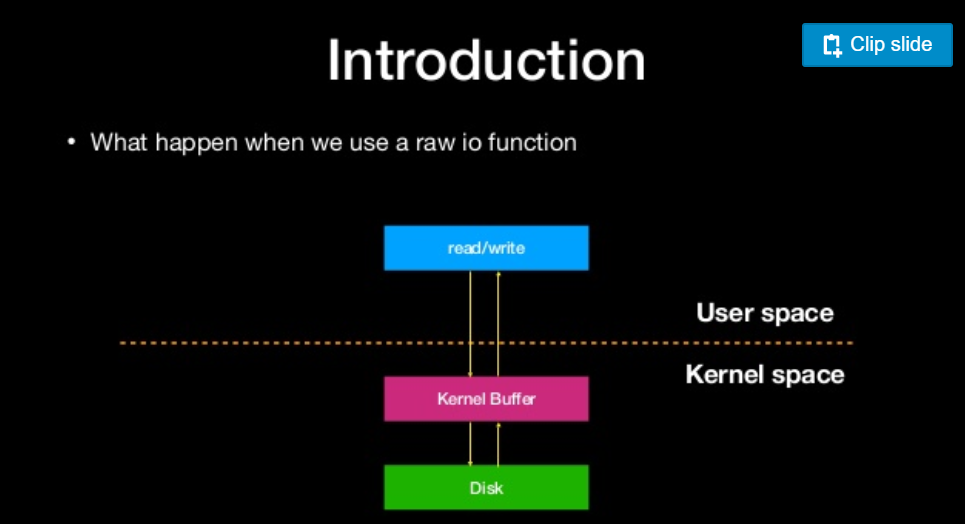
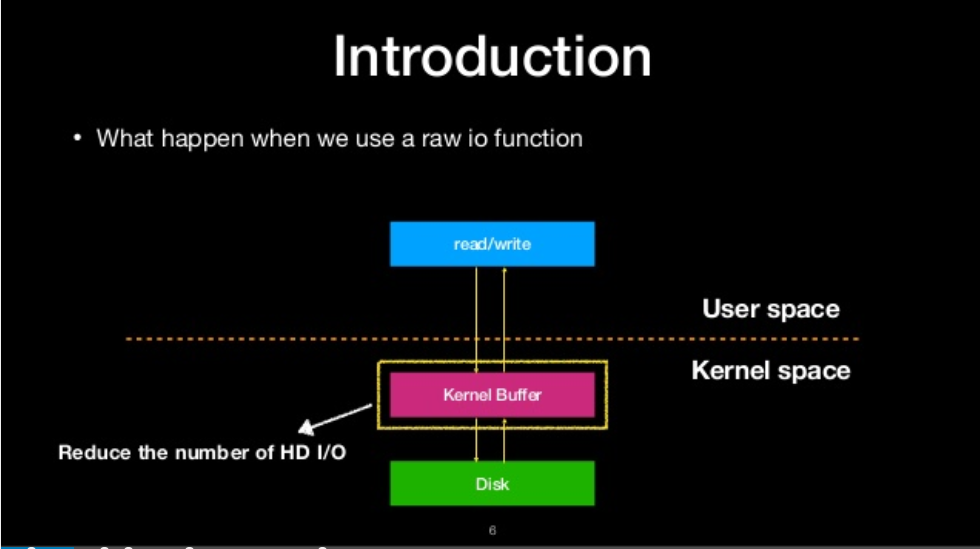
what is file stream?
- A higher-level interface on the primitive file descriptor facilites
- Stream buffering
- Portable and High performance
what is FILE structure
- A file stream descripor
- Created by fopen
what happen when we use stdio function
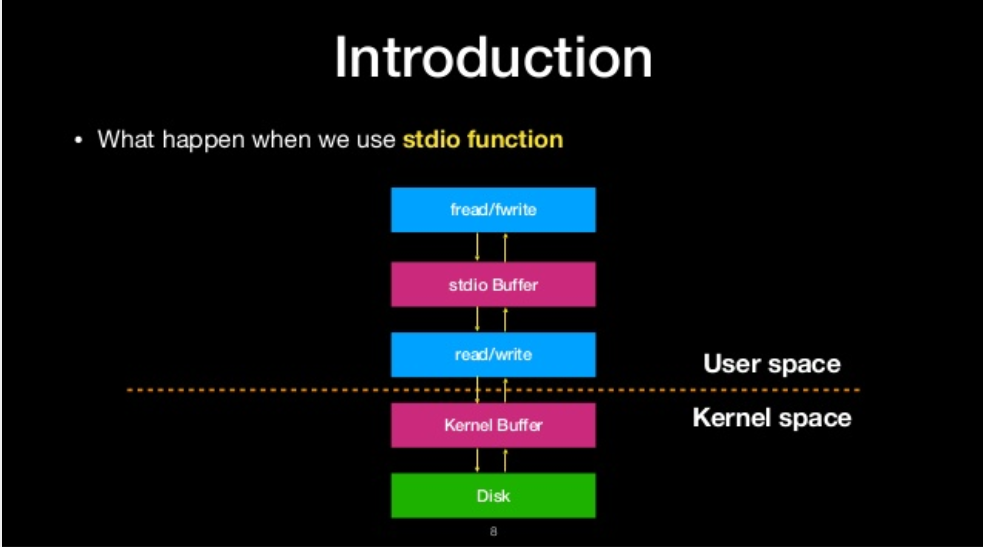
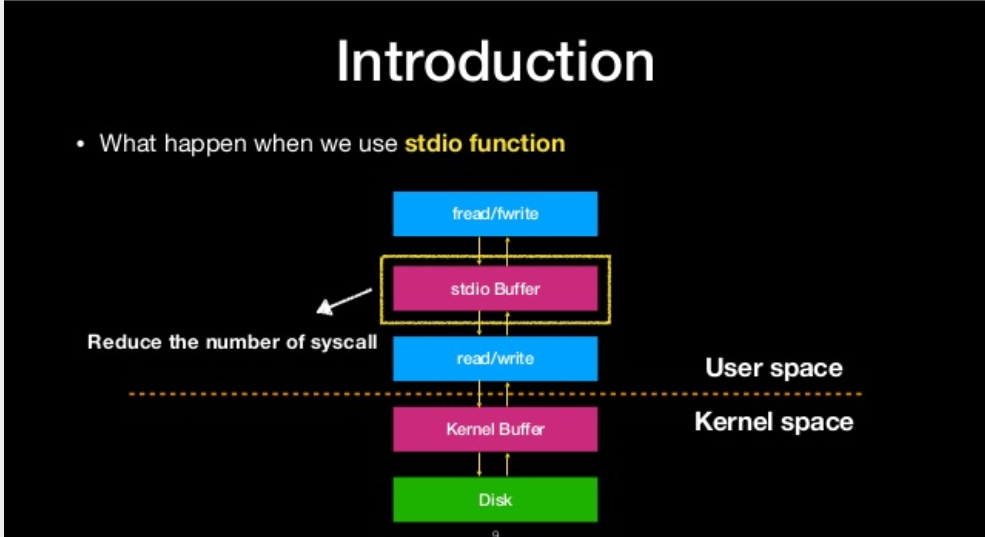
overwrite the file struction
- File struction
- A complex struction
- Flags
- Stream buffer
- File descriptor
- FILE_PUTS
- virtul function table
- A complex struction
结构体在我之前的文章有写,师傅们可以看之前的文章即可
flags
- Record the attribute of the File stream
- Read only
- Append

Stream buffer
- Read buffer
- Write buffer
- Reserve buffer

_fileno
- File descriptor
- Return by sys_open

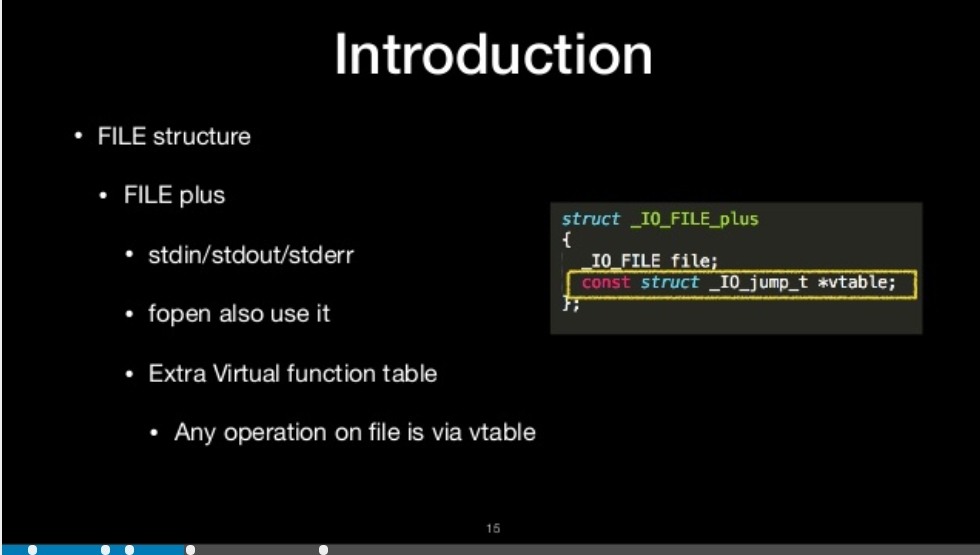
file_plus
- stdin/stdout/stderr
- fopen also use it
- Extra Virtul function table
- Any operation on file is via vtable

chain
Every FILE associate with a _chain (linked list)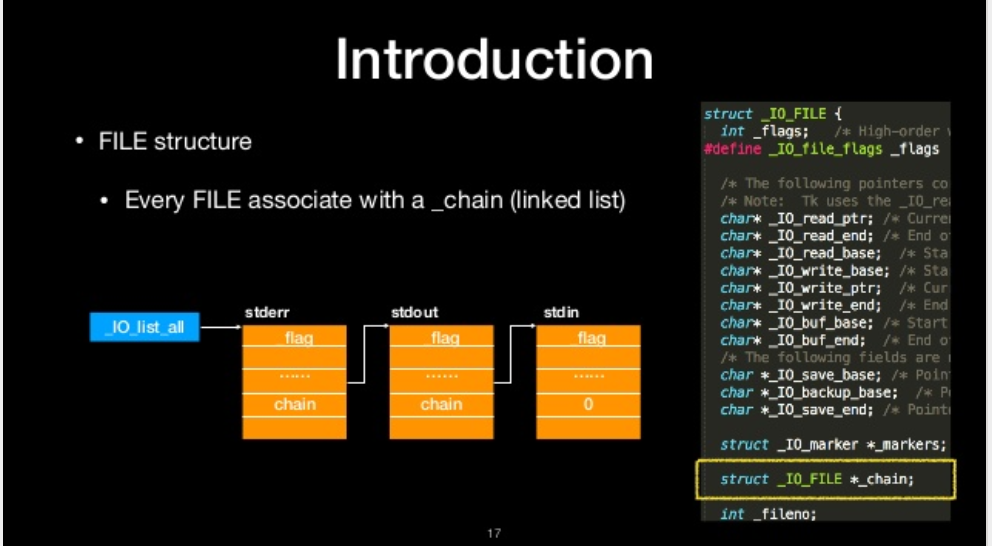
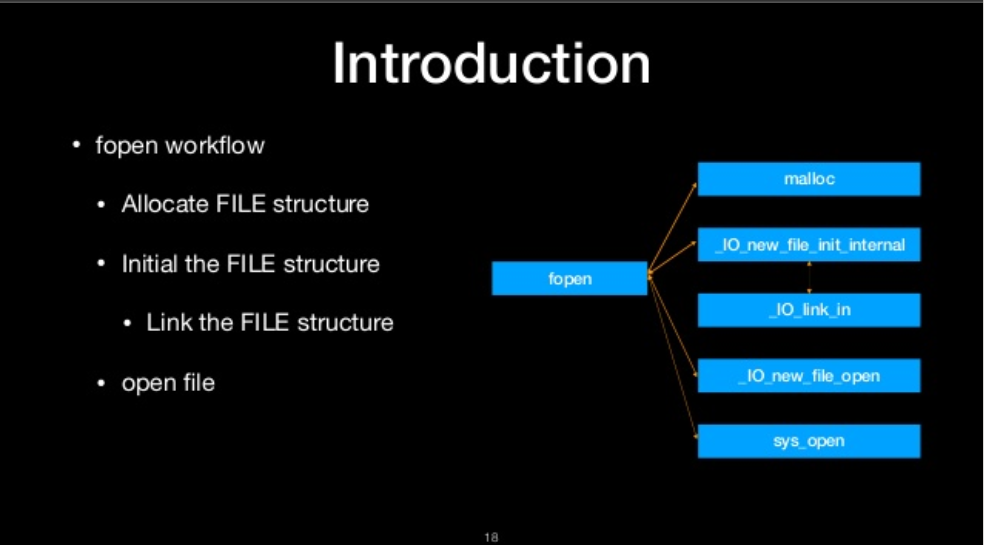
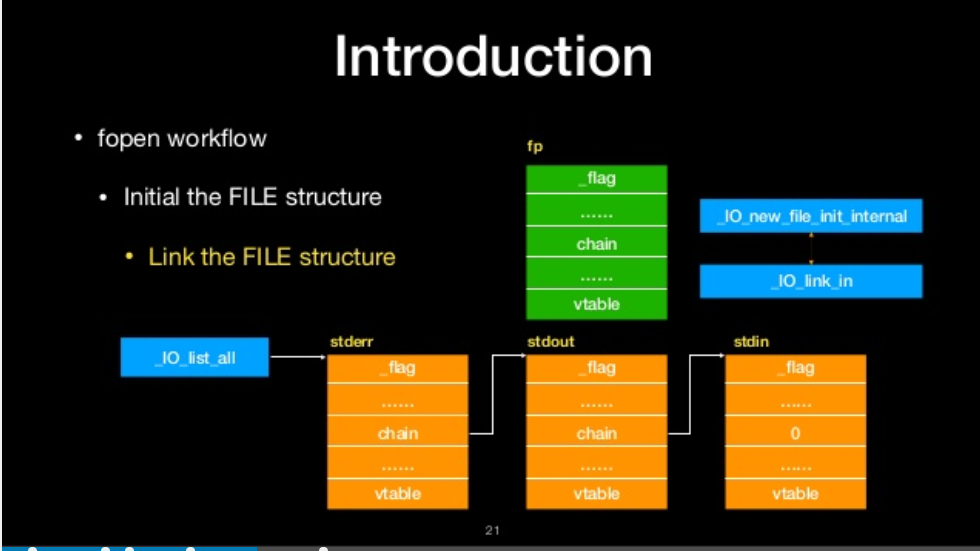
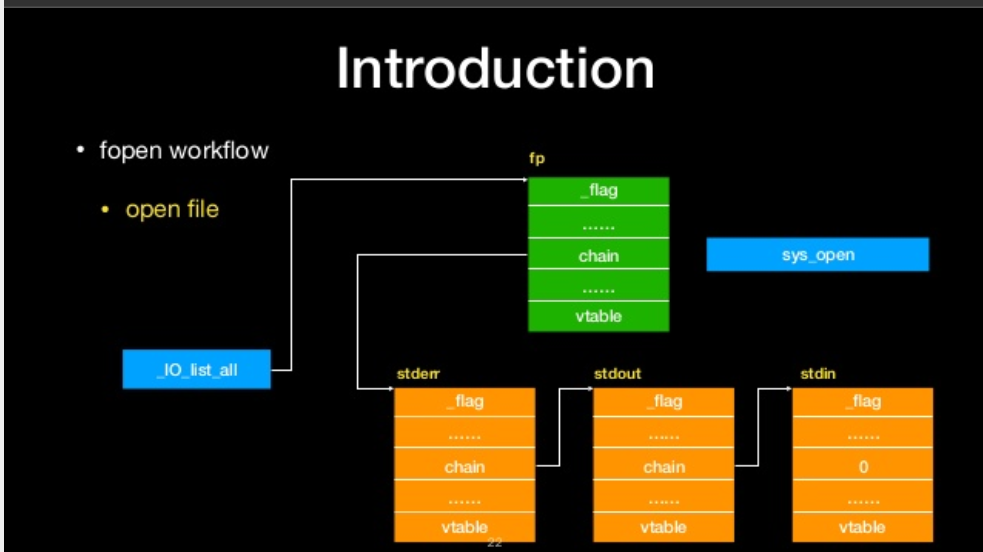
fopen workflow
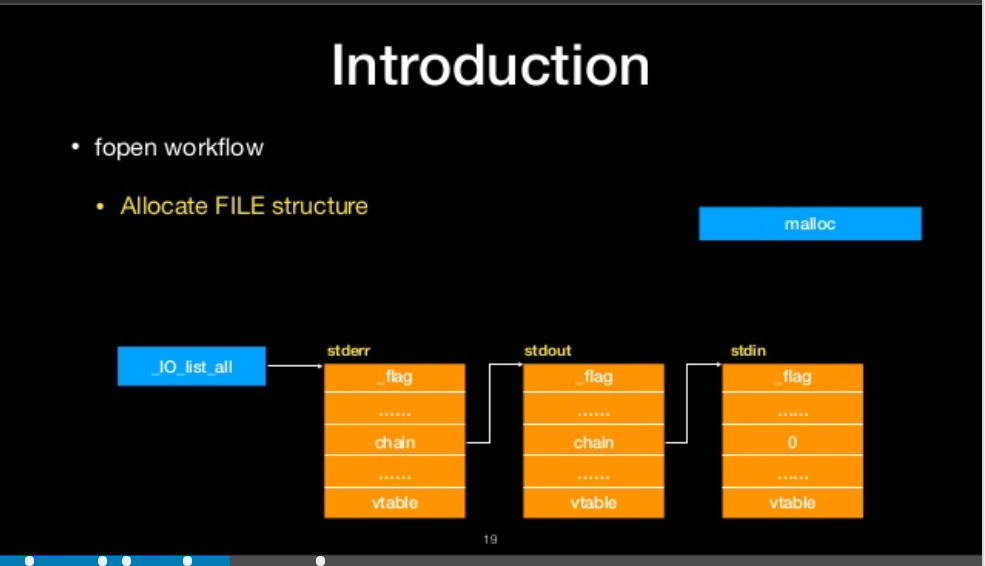
- Allocate FILE Structure
- initial the FILE structure
- Link the FILE structure
- open file
allocate file structure
initial the file structure
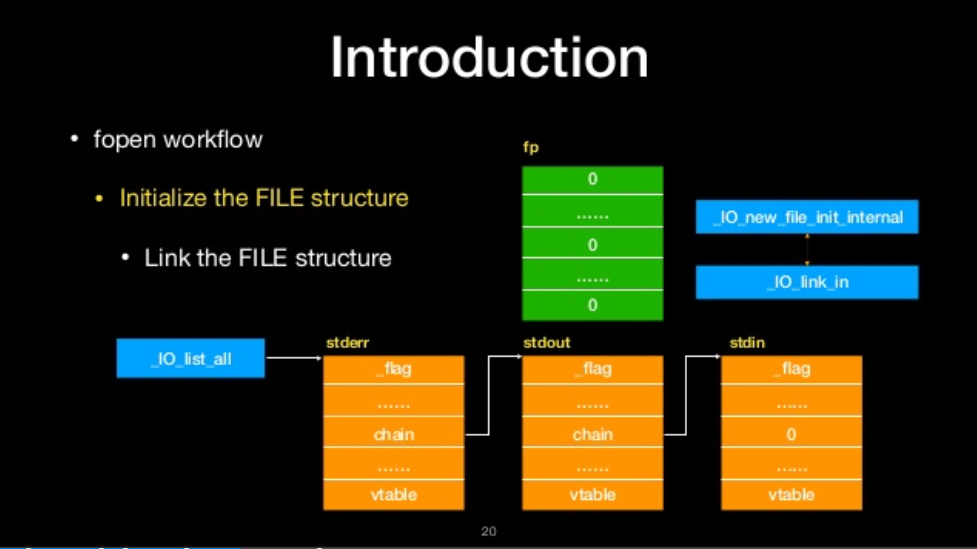
Link the file structure
open file
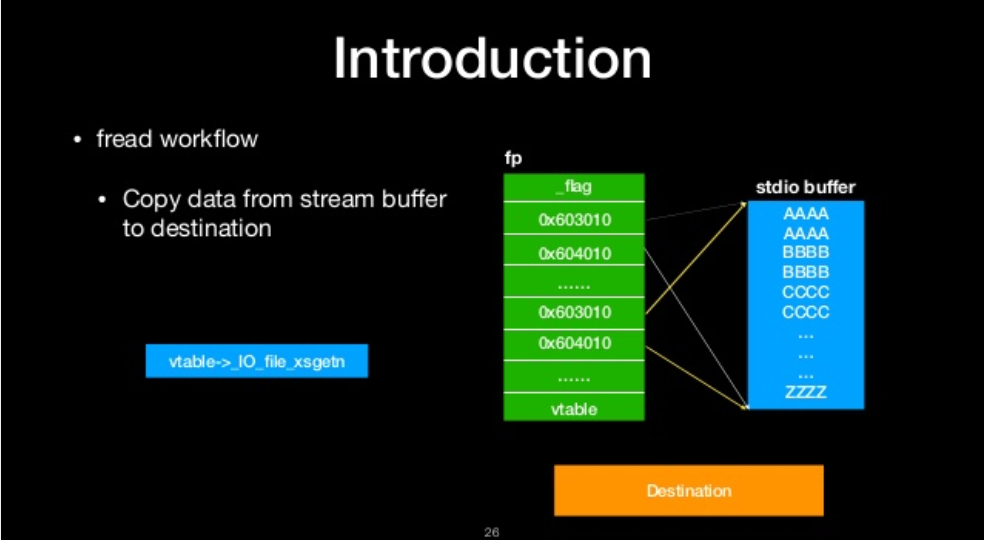
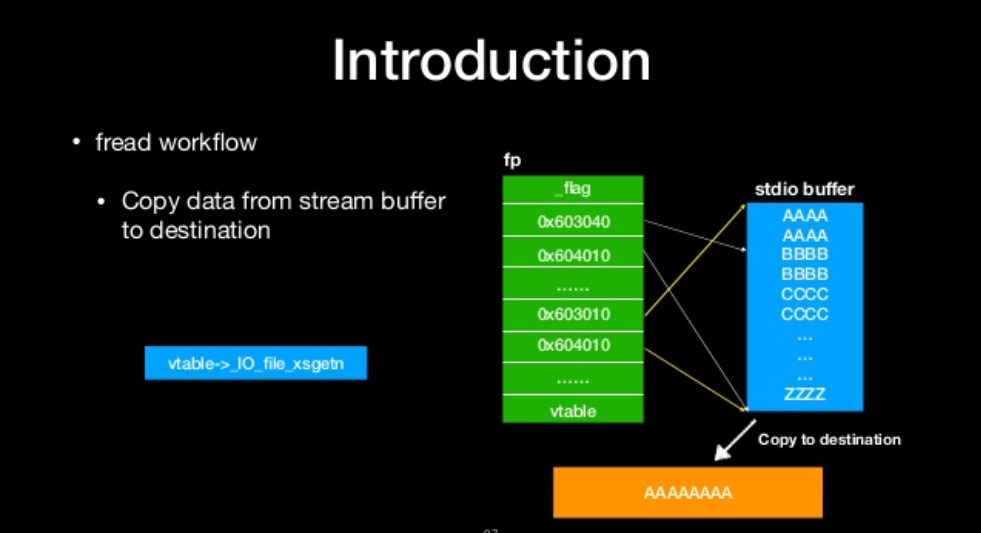
fread workflow
- IF stream buffer is NULL
- Allocate buffer
- Read data to the stream buffer
- copy data from stream buffer to destination

If stream buffer is NULL
allocate buffer
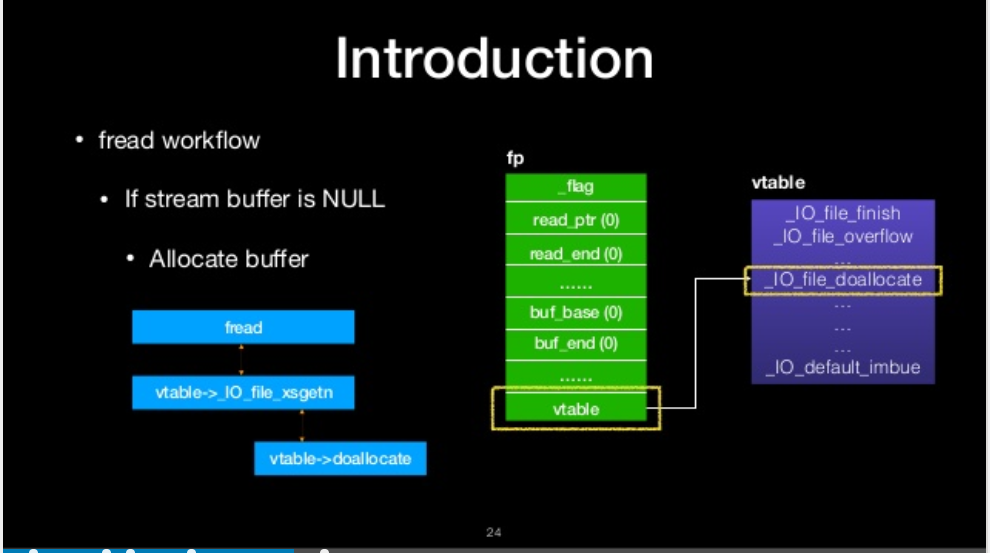
read data to the stream buffer
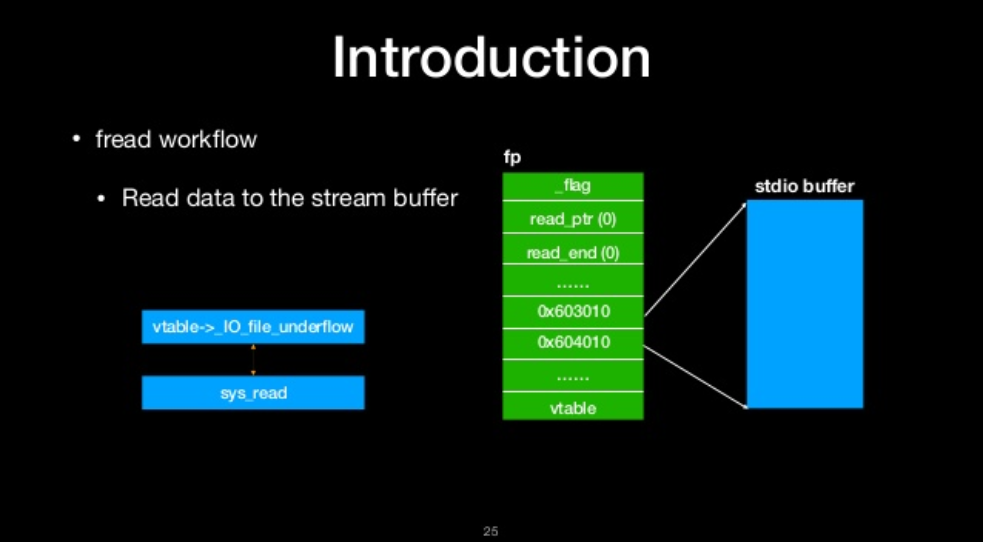
copy data from stream buffer to destination
if the stream is filled or flush the stream
- write data from stream buffer to the file

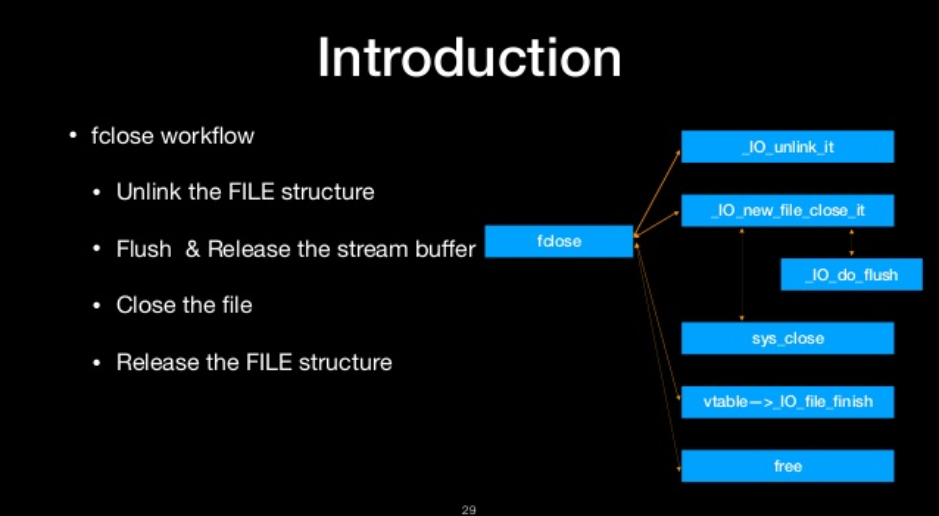
fclose workflow
- If stream buffer is NULL
- allocte buffer
- copy user data to the stream buffer
- if the steram buffer if filled or flush the stream
- write data from stream buffer to the file

- unlink the file structure
- flush & realease the strean buffer
- close the file
- release the file structure
Exploitation of FILE structure
There are a good target in FILE structure
Virtual function table
1 | |
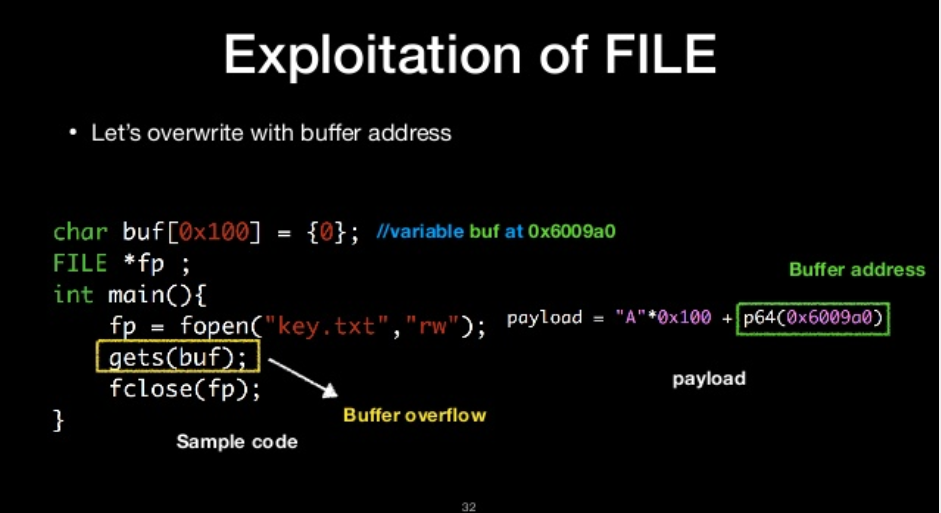
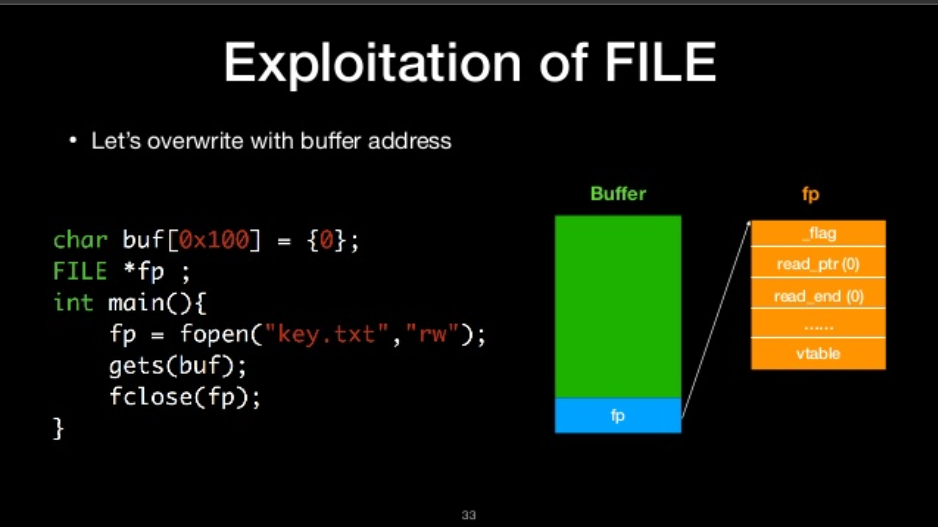
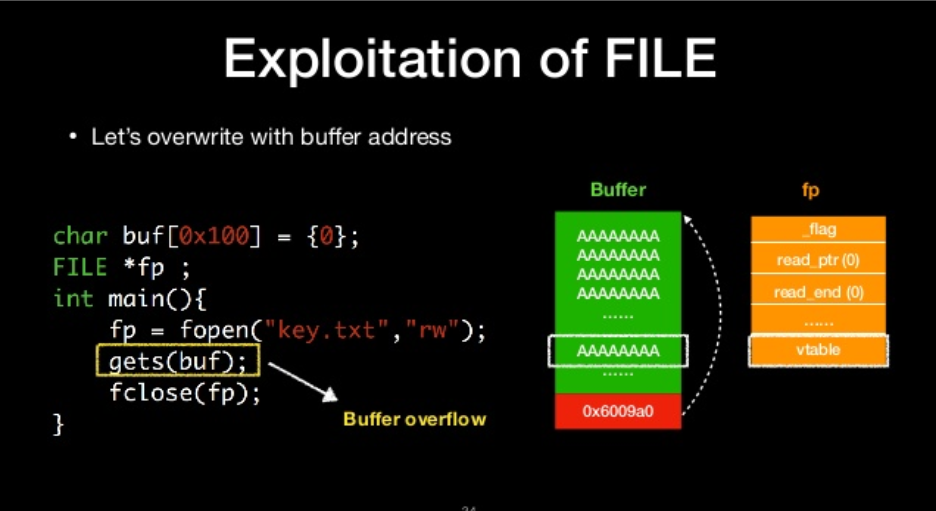
let’s overwrite with buffer address
Not call vtable directly
- RDX is our input but not call instruction
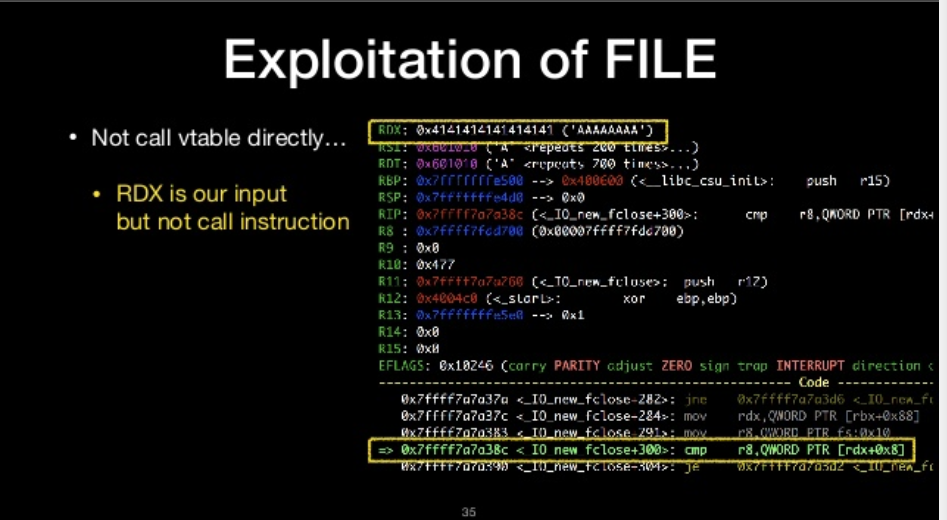
Let’s see what happened in fclose
- we can get information of segfault in gdb and located it in source code
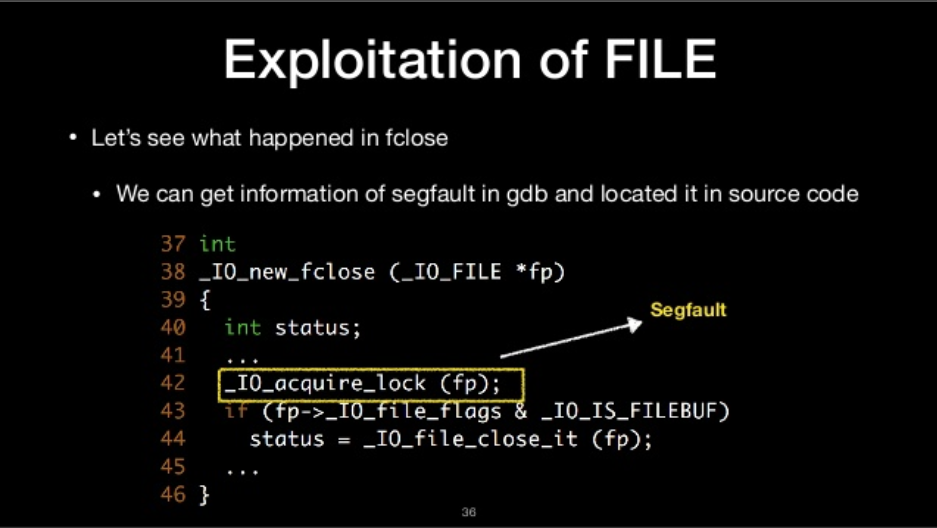
File structure
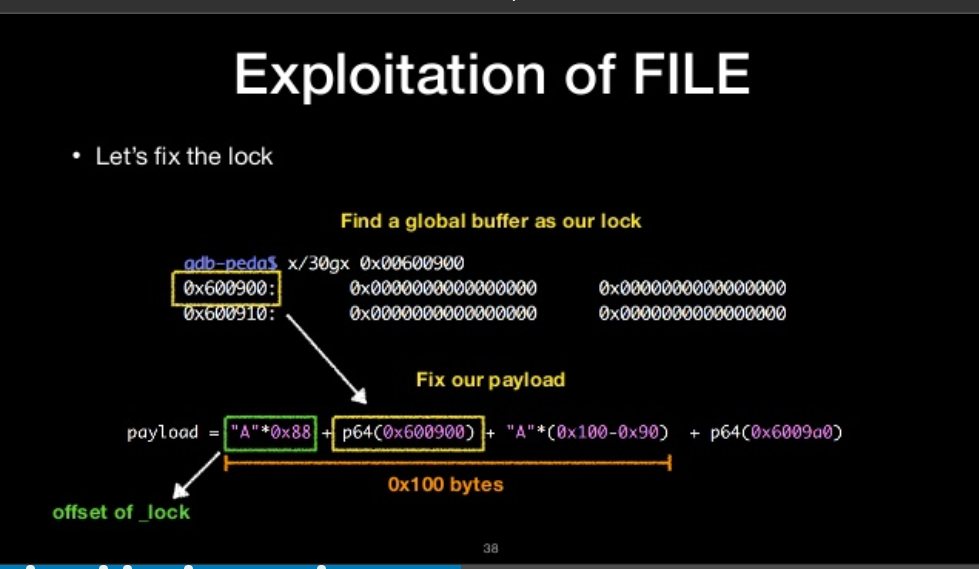
- _lock
- prevent race condition in multithread
- Very common in stdio related function
- Usually need to construct it for Exploitaion

Let’s fix the lock
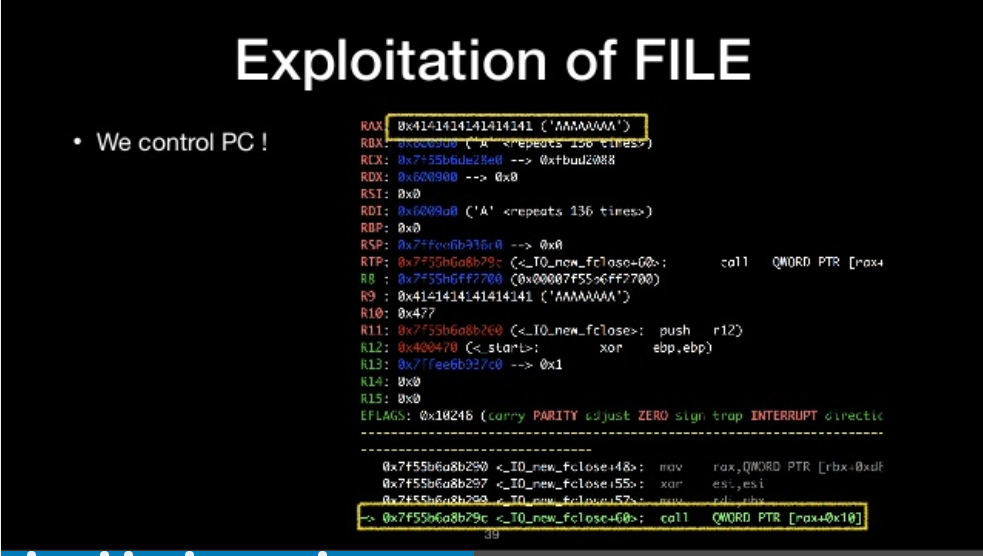
we control PC
Another interesting
- stdin/stdout/stderr is also a FILE struct in glibc
- We can overwrite the global variable in glibc varible in glibc to control the flow

FSOP
- File-Stream Oriented Programing
- Control the linked list of File stream
- _chain
- _IO_list_all
- Powerful function
- _IO_flush_all_lockp
- Control the linked list of File stream
_IO_flush_all_lockp
- flush all file stream
We can call it
- glibc abort routine
- exit function
- Main return
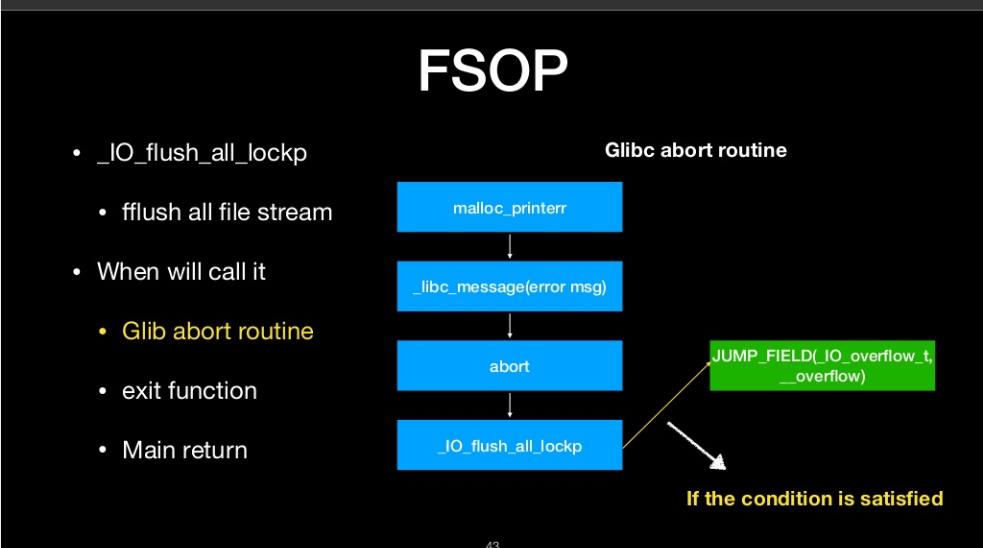
- It will process all FILE in FILE linked list
- We can construct the linked list to do oriented programing

FILE-stream oriented programing

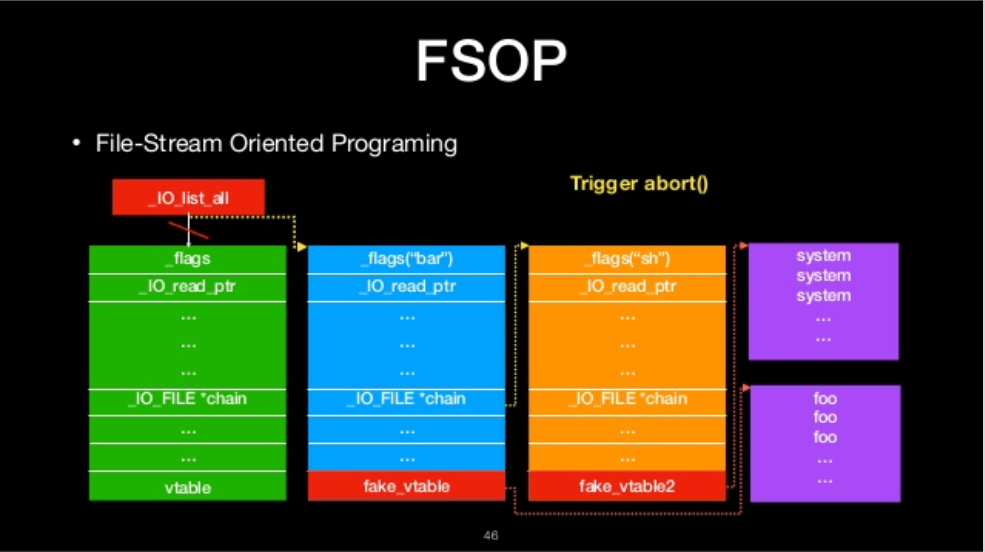
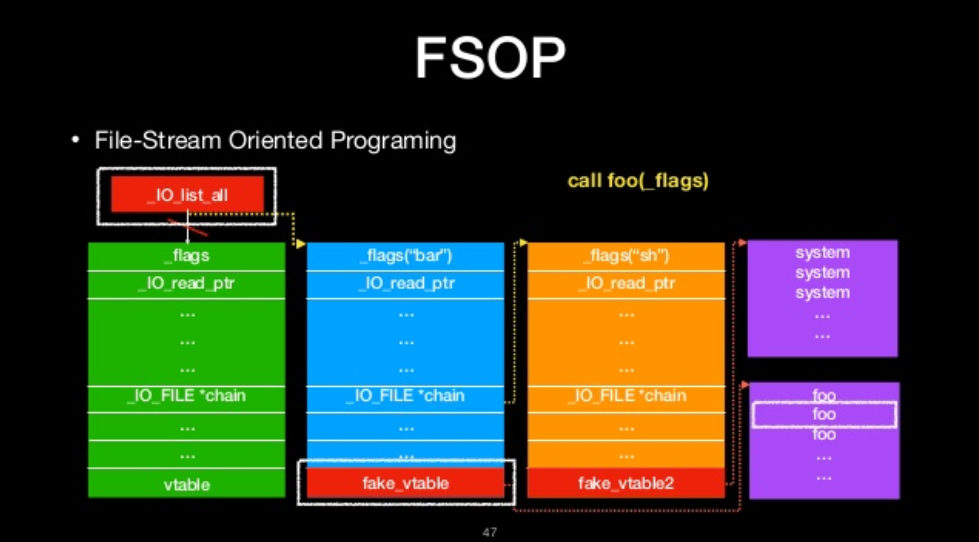
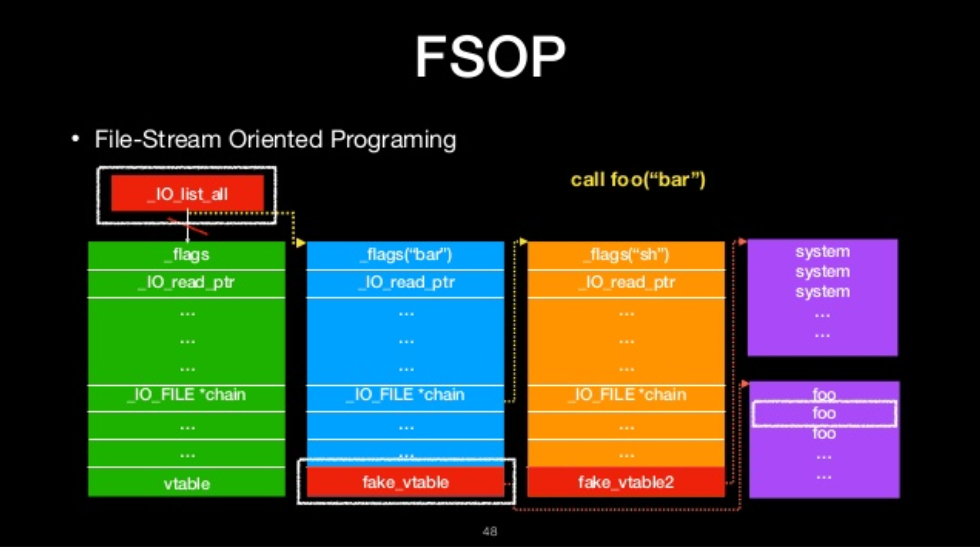
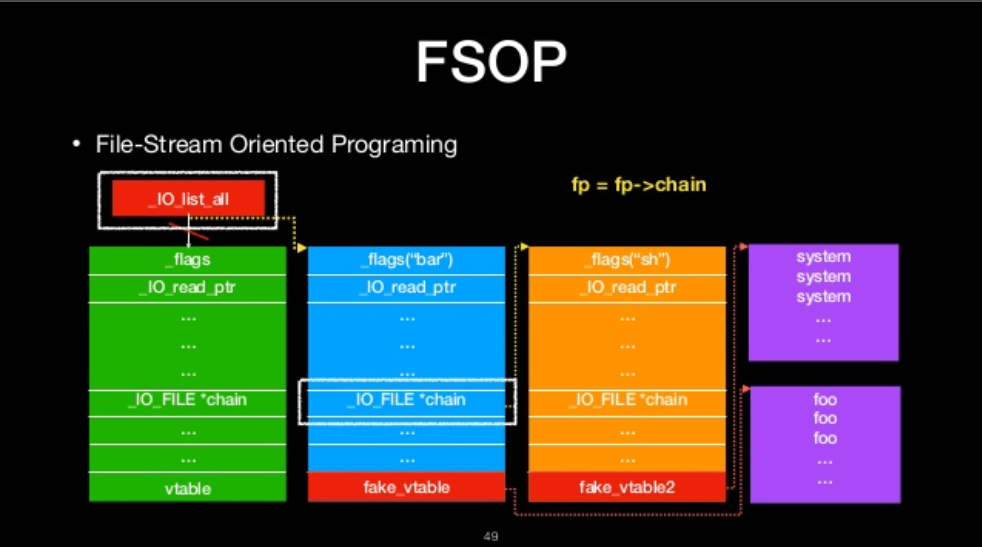
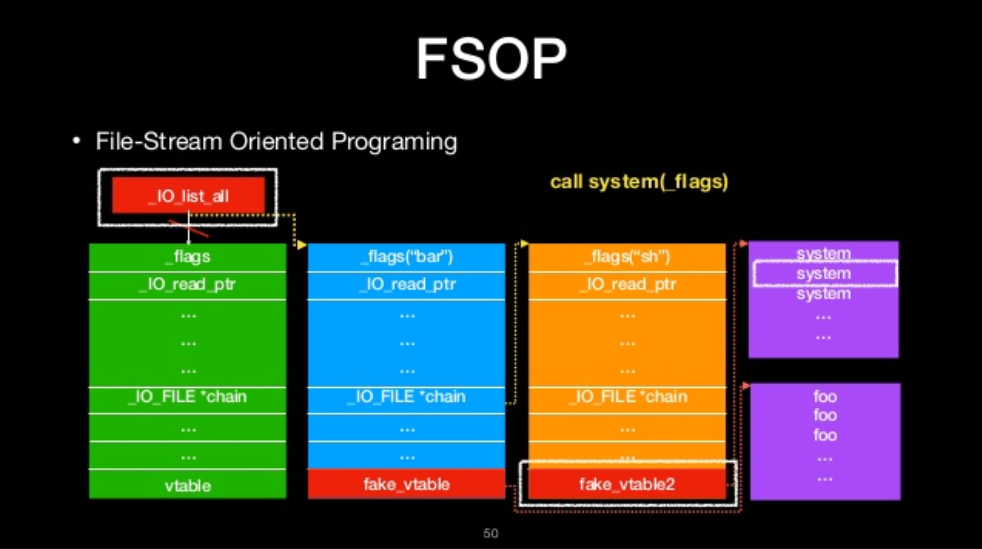
The we will ge shell!
Vtable verfication in FILE structure
- Unfortunately, there are a virtual function table in latest libc
- Check the address of vtable before all virtual function call
- If vtable is invalid, it would abort
Vtable verification
- Vtable verification in File
- The vtable must be in libc _IO_vtable section
- If it’s not in _IO_vtable section, it will check if the vtable are permitted
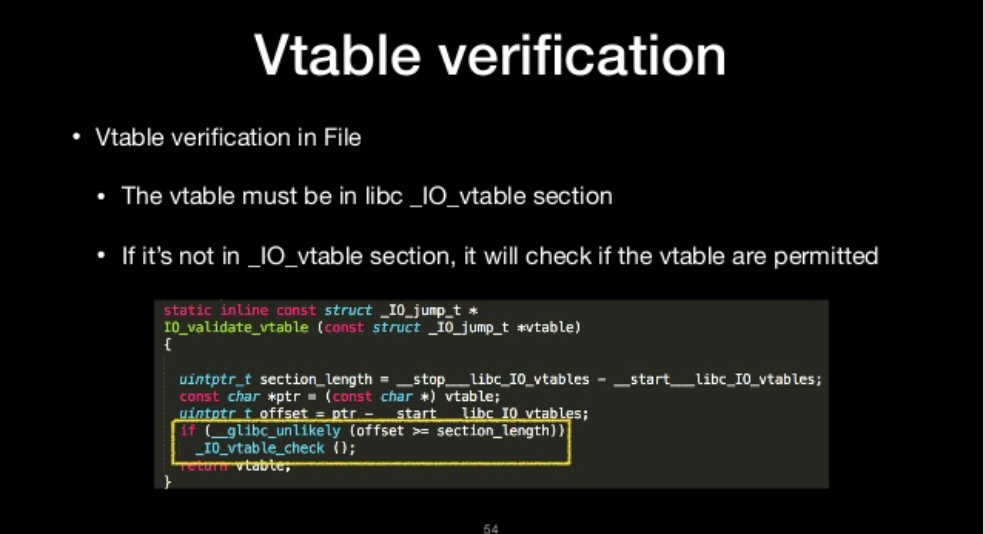
_IO_vtable_check
- Check the foreign vtables Vtable verification
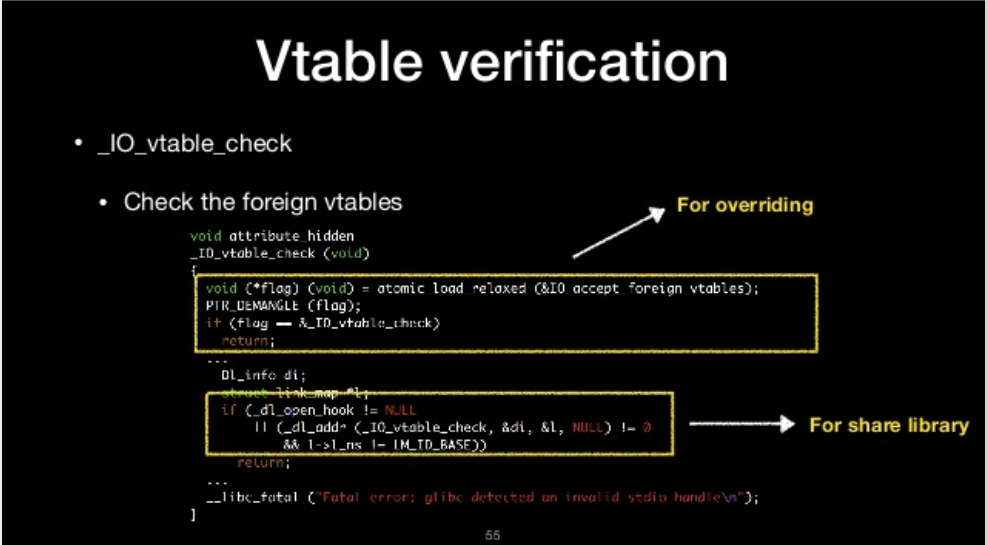
BPASS
- Overwrite IO_accept_foreign_vtables ?
- It’s very difficult because of the pointer guard

- Overwrite _dl_open_hook ?
- Sounds good, but if you can control the value, you can also control other good target
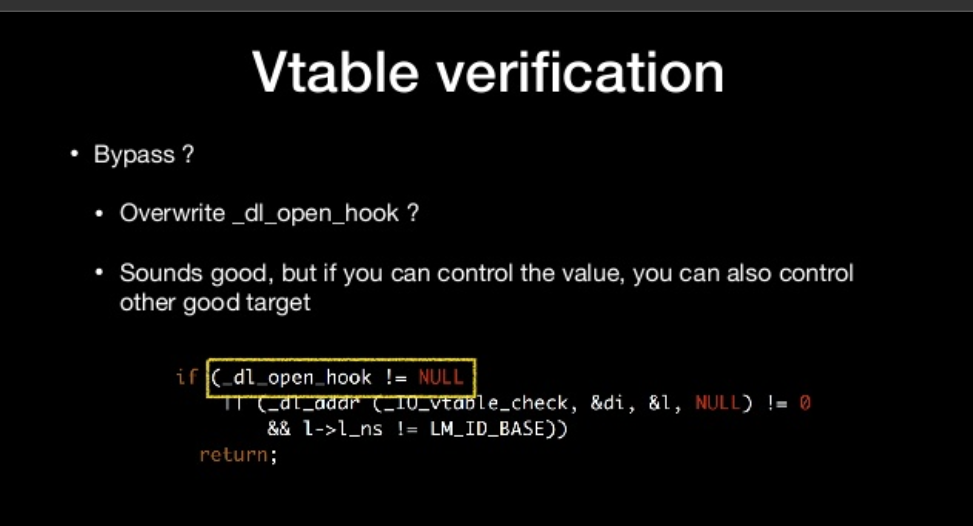
Summary of the vtable verification
- It very hard to bypass it
- Exploitation of FILE structure is died ?
Make file structure greate again
how about change the target from vtable to other element
- stream buffer & File Descripor

- If we can overwrite the FILE structure and use fread and fwrite with the FILE structure
- We can
- Arbitrary memory reading
- Arbitrary memory writing
Arbitrary memory reading
- fwrite
- Set the _fileno to the file descriptor of stdout
- Set _flag & ~_IO_NO_WRITES
- Set _flag |= _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING
- Set the write_base & write_ptr to memory address which you want to read
- _IO_read_end equal to _IO_write_base
其中:
- Set _flag &~ _IO_NO_WRITES
- Set _flag |= _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING
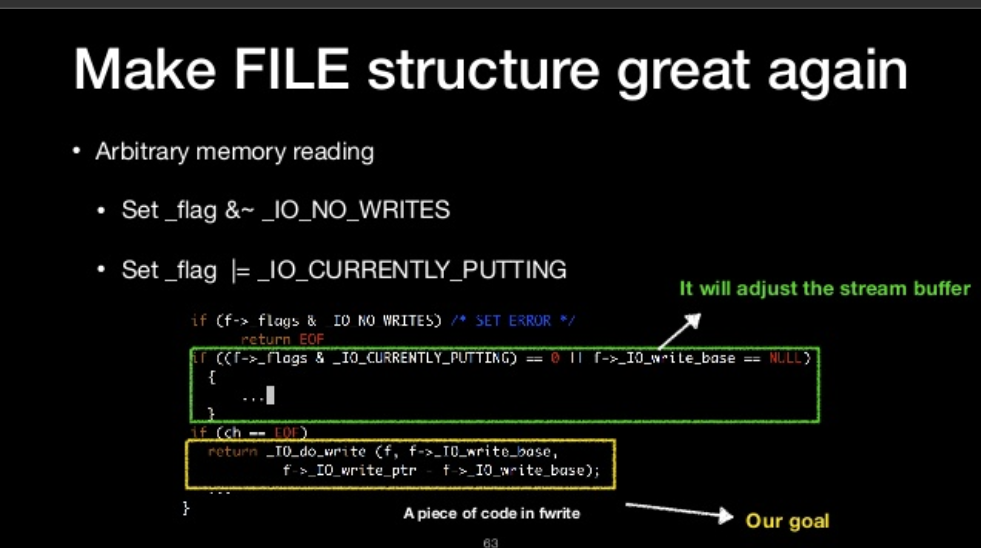
- Let _IO_read_end equal to _IO_write_base
- If it’s not, it would adjust to the current offset

sample code

- fread
- Set the _fileno to file descriptor of stdin
- Set _flag &~ _IO_NO_READS
- Set read_base & read_ptr to NULL
- Set the buf_base & buf_end to memory address which you want to wirte
- buf_end - buf_base < size of fread
其中:
- Set read_base & read_ptr to NULL
- Set _flag &~ _IO_NO_READS
sample code
If you have arbitrary memory address read and write, you can control the flow very easy
- GOT hijack
- _malloc_hook/_free_hook/_realloc_hook
- …
By the way, you can not only use fread and fwrite but also use any stdio related function
If we don’t have any file operation in the program,We can use:
- stdin/stdout/stderr
- put/printf/scanf
- …
Scenario
- use any stdin related function
- scanf/fgets/gets
- Stdin in unbuffer
- very common in normal stdio program
- use any stdin related function
- Overwrite buf_end with a pointer behind the stdin
- Unsorted bin attack
- Very common in heap exploitation
- stdin relatedd function
- scanf(“%d”,&var)
- It will call
- read(0,buf_base,sizeof(stdin buffer))
- It will call
- scanf(“%d”,&var)
- It can overwrite many global variable in glibc
- Input :aaa…
Control The PC
- How about Windows ?
- No vtable in FILE
- It also has stream buffer pointer
- You can corrupt it to achieve arbitrary memory read and write
Conclusion
FILE structure is a good target for binary exploit
- It can be used to
- Arbitrary memory read and write
- Control the PC and do oriented programing
- Other exploit technology
- Arbitrary free/unmmap
- It’s very powerful in some unexploitable case
- Let’s try to find more and more exploit technology in FILE structure!
over~
- It can be used to
play withe file structure(搬运)
https://nightrainy.github.io/2019/08/07/play-withe-file-structure-搬运/